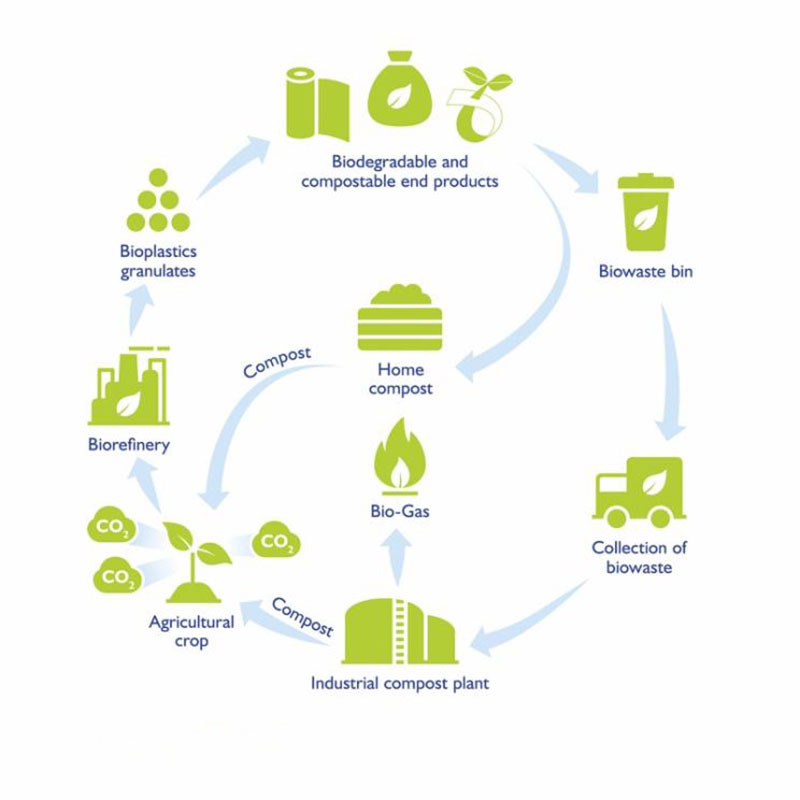
All production processes implement the principles of green and clean production; promote resource regeneration and feed the natural environment.
Since 1950 to date, approximately 8.3 billion tons of plastics have been discarded worldwide. The global collection and recycling rates of waste plastics have been at a low level and are generally unable to meet disposal needs. The plastic circular economy is a development model that redefines production and consumption, mainly including: designing from the source to eliminate resource waste and environmental pollution, promoting easy-to-recycle and recyclable designs, and increasing the proportion of recycled content; implementing reuse to extend the life cycle of products and materials; implementing green and clean production principles in all production processes; and promoting resource recycling to feed the natural environment.
Since 1950, the world has produced more than 6 billion tons of plastic, 79% of which went into landfills or the natural environment, and only 9% was recycled. Plastics will continue to be used and exist for a long time in our foreseeable future. Therefore, we need to implement the “3R” principle in all aspects and processes of plastic production, distribution and consumption, i.e., “Reduce, Reuse and Recycle”.
According to the “3R” principle of circular economy, the first is “Reduce”, reduce the production and use of disposable plastic products as much as possible, and vigorously promote the ecological design of plastic products from the source, such as easy to recycle and regenerate; the second is “reuse”, in the circulation and consumption link, explore recyclable plastic products and business models; finally, “resource“, in the end of the disposal link, to carry out the recycling and materialization of waste plastic products, for the time being do not have the materialization conditions for the use of Energy recycling.