Specific division of degradable materials
1, photodegradable materials:
refers to the degradation can occur under the action of light, obtained through chemical synthesis or the addition of photosensitizers. This material avoids the problem of environmental pollution caused by plastic incineration, but its degradation process, light as the main element of degradation, has a significant impact on the degradation effect. When buried in soil, the expected degradation will not be achieved due to the lack of light. At present, it is mainly used in two aspects: packaging materials and agricultural films.
2、Biodegradable material:
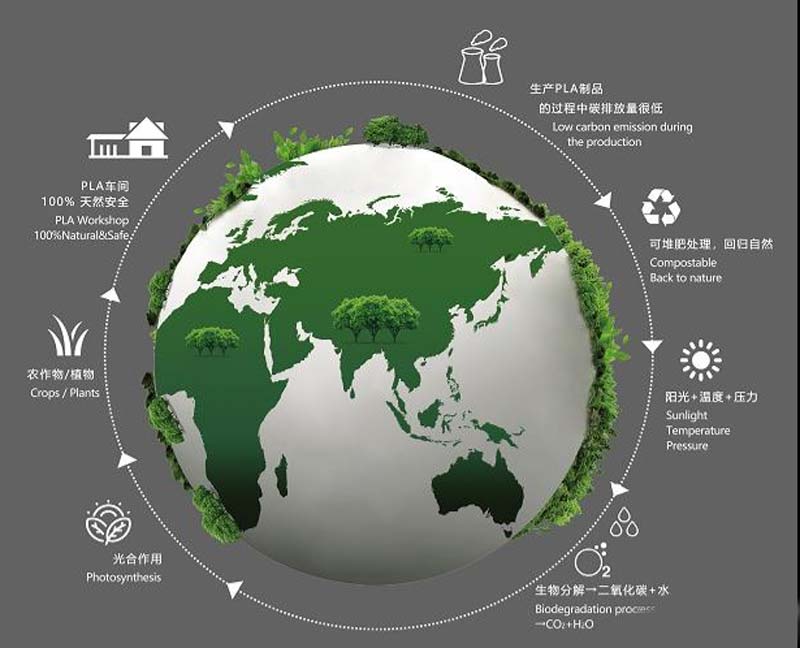
It is one of the more widely used and more abundant on the market at present. It mainly contains polylactic acid (PLA, poly-3-hydroxyalkanoate (PHA, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) and other materials. Biodegradable lunch boxes made from PLA composite film combined with pulp molded tableware are generally made from natural plant fibers, which can form carbon dioxide and water under the action of microbial decomposition over a period of time in the natural environment. Usually these microorganisms include bacteria, fungi, algae, etc. Even if it is discarded inside the soil, lunch boxes made of this material can be degraded under the action of microorganisms. The major difference with plastic is that it can be biologically regenerated, and the material is recycled, which will not cause pollution to land organisms, marine organisms and other environments and reduce the damage to the soil. At present, there are achievements in food packaging, medical packaging and industrial packaging.
3, environmental degradation materials:
in the light, heat pollution compounds, microorganisms, insects, mechanical forces and other natural environmental conditions degradation. This kind of material generally includes natural plants, some synthetic materials, etc. At present, completely degradable materials are very common in daily life, such as thermoplastic biodegradable plastics (PBAT), polylactic acid (PLA) and polyhydroxy fatty acid esters (PHA), etc.